What Is PLC Automation?
Factories buzz with activity. Steel slabs roll through mills, sugar cane churns into syrup, and power flows through distribution lines. Behind these complex operations, quiet technology keeps everything running smoothly: PLC automation. Short for Programmable Logic Controller Automation, it’s like the brain of a factory, controlling machines with precision to boost efficiency, ensure safety, and cut errors. For plant managers and engineers, understanding PLC automation is the key to unlocking smarter, more reliable operations in industries like steel, sugar, and power distribution.
At its heart, PLC automation uses rugged, specialized computers to automate tasks and monitor processes in real time. These systems are the backbone of modern manufacturing, replacing manual controls with speed and accuracy. Fuji Gemco, a leader in PLC automation, crafts solutions that empower businesses to thrive in demanding environments. Whether a hot rolling mill or a paper plant, PLC automation simplifies operations and drives results. Let’s dive into what makes PLC automation essential, how it works, and why it’s transforming industries worldwide.
The Basics of PLC Automation Explained
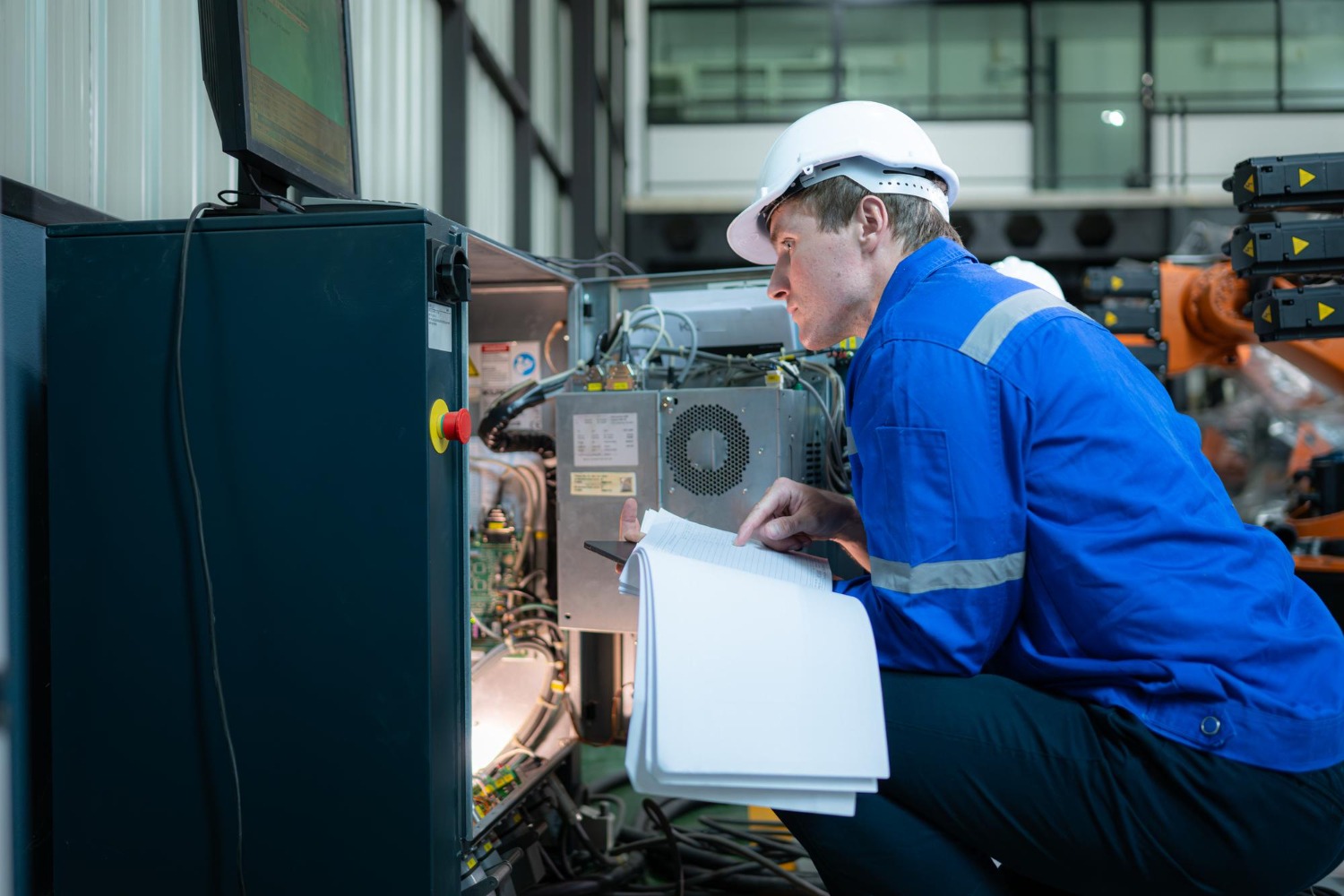
A PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is a rugged, specialized computer used in PLC automation to control industrial machines and processes. It’s like the brain of a factory, designed to handle harsh environments like dust, heat, or vibration while ensuring precision and reliability. PLCs take inputs from sensors (e.g., temperature or speed), process them using programmed instructions, and send commands to equipment (e.g., start a motor or stop a conveyor).
Here’s one core component of PLC automation:
- Programmable Logic Controller (PLC): A durable computer that reads sensor inputs (e.g., temperature), processes them with custom logic, and sends commands to machines (e.g., adjust motor speed).
This simplicity of reading inputs, processing, and acting makes PLC automation a game-changer in industries where reliability is critical.
How PLC Automation Works?
PLC automation operates in a cycle of sensing, thinking, and doing. Sensors collect data from machines, and the PLC processes it and controls equipment or alerts operators. For example, in a TMT bar mill, PLC automation might detect a steel slab moving too fast and slow the rollers to prevent damage. The process is seamless, fast, and reduces human error.
Here are three key steps in PLC automation:
- : Sensors monitor speed, pressure, and temperature.
- : The PLC uses programmed logic to analyze data and decide actions.
- : Sends commands to machines, like stopping a motor or adjusting a valve.
This cycle ensures PLC automation keeps operations smooth and responsive.
Benefits of PLC Automation for Industries
PLC Automation transforms factories, delivering efficiency, safety, and insights. Workers can focus on strategy and innovation by automating repetitive tasks and monitoring processes. PLC automation is a lifeline for industries like steel or sugar, where precision is non-negotiable.
Here are the five significant benefits of PLC automation:
- Increased Efficiency>: It automates tasks, reducing downtime and boosting output in rolling mills.
- Enhanced Safety: Detects hazards, like equipment faults, and acts instantly to protect workers.
- Reduced Errors: Eliminates manual mistakes, ensuring consistent product quality.
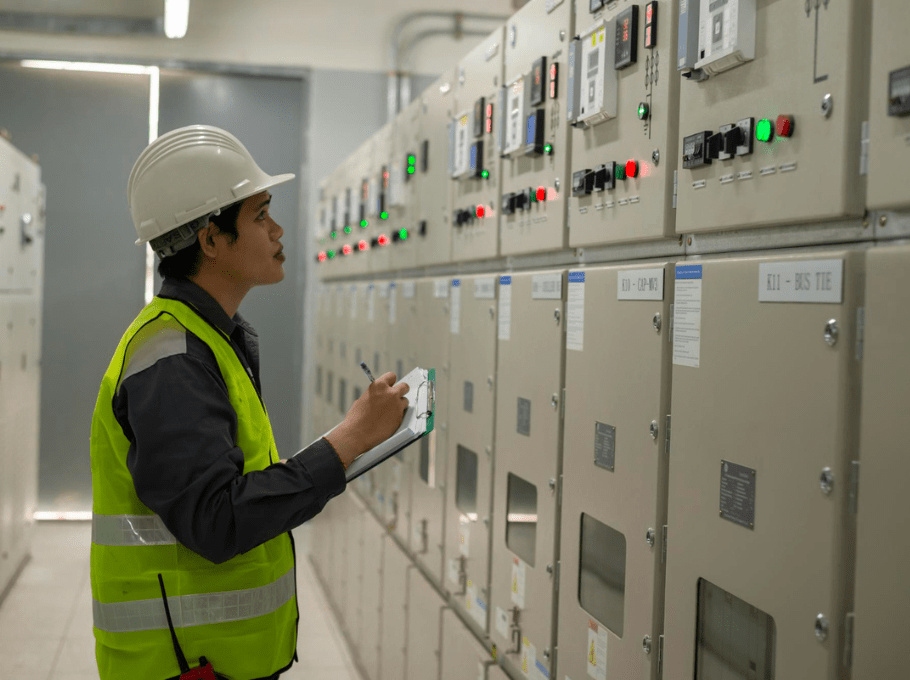
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides live data for quick power distribution decisions.
- Cost Savings: Lower maintenance and labor costs through reliable automation
These advantages make PLC automation essential for competitive industries.
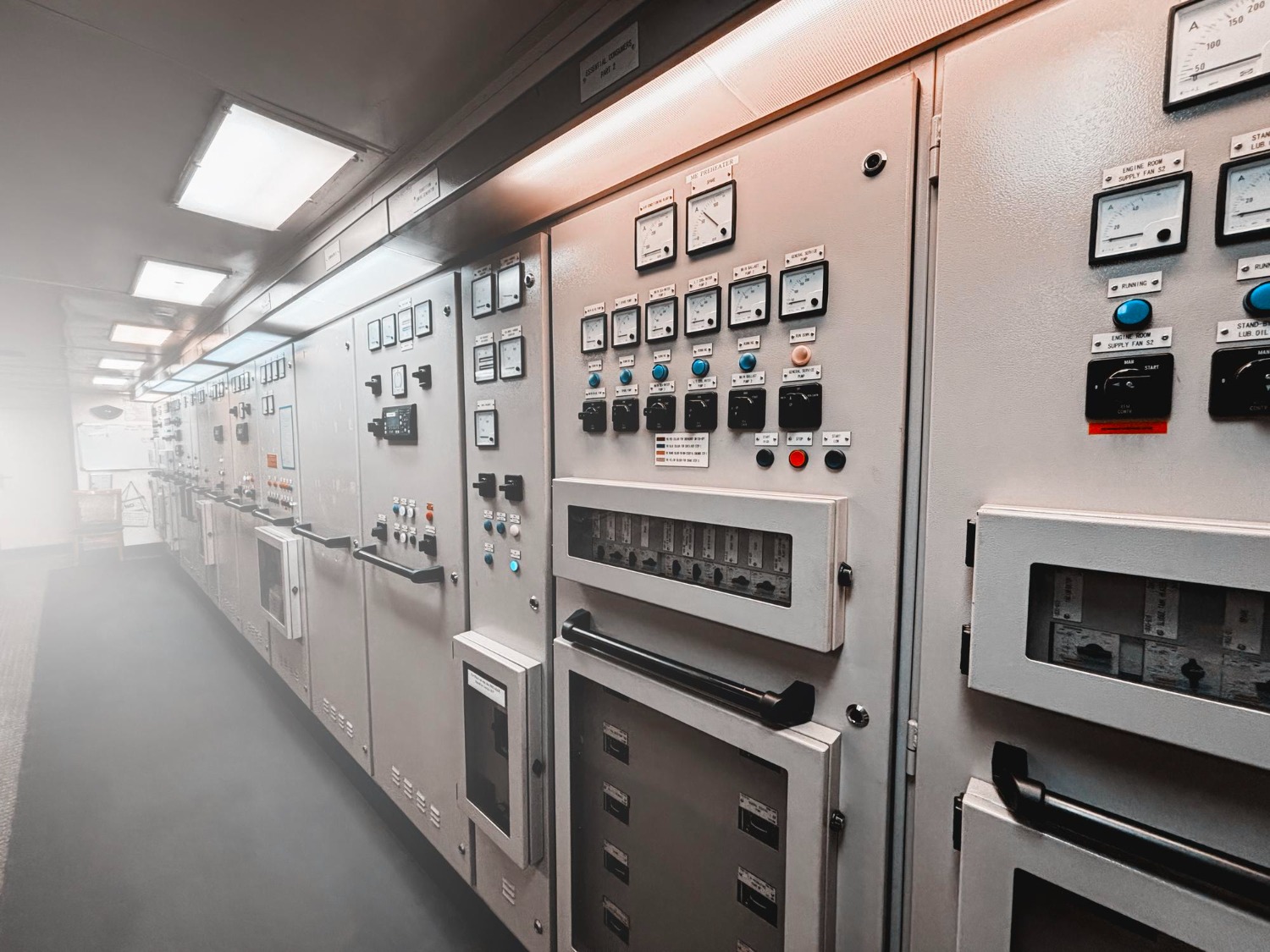
Key Components of PLC Automation Systems
A PLC automation system is more than just a PLC. It’s a network of tools working together. From sensors to software, each part helps keep operations efficient. Fuji Gemco’s systems, for example, integrate advanced PLCs with user-friendly software for maximum impact.
Here are seven components of a typical PLC automation system:
- PLC Unit: The core controller processes inputs and outputs.
- Sensors: Devices measuring temperature or speed.
- Actuators: Equipment like motors or valves controlled by PLC.
- Input/Output Modules: Connect the sensors and actuators to the PLC.
- Power Supply: Ensures steady operation in harsh environments.
- Programming Software: Tools to customize PLC logic for specific tasks.
- SCADA Software: Displays data and enables remote monitoring, like Fuji Gemco’s NISDAS.
These components create a robust PLC automation ecosystem.
Applications of PLC Automation
PLC automation is versatile, powering diverse industries with tailored solutions. Whether controlling high-speed steel rollers or monitoring sugar boiling, PLC automation adapts to unique challenges, ensuring reliability and precision.
Here are nine industries transformed by PLC automation:
- Hot Rolling Mills: Manage tension-free rolling for high-quality steel.
- Cold Rolling Mills: Ensure precise thickness and surface quality.
- TMT Bar Mills: Optimizes high-speed rebar production.
- Sugar Mills: Controls volatile processes like cane crushing.
- Paper Mills: Streamlines production for consistent output.
- Power Distribution: Monitors and stabilizes the energy flow.
- Cable & Wire Industries: Enhance manufacturing precision.
- Textile Plants: Automated weaving and dyeing processes.
- Cement Factories: Manages kilns and material handling.
This broad applicability underscores why PLC automation is indispensable.
Why PLC Automation Matters Today
In today’s fast-paced world, industries face pressure to produce more, faster, and safer. PLC automation meets these demands by streamlining operations and providing data-driven insights. It’s not just about keeping up. It’s about staying ahead in a competitive market.
Here are three reasons PLC automation is critical now:
- Industry 4.0 Alignment: Supports smart factories with IoT and data integration.
- Sustainability: Reduces waste and energy use, like in paper mills.
- Workforce Efficiency: Frees workers from repetitive tasks for higher-value roles
As industries evolve, PLC automation is the foundation of progress.
Challenges and Solutions in PLC Automation
While PLC automation is powerful, it’s not without challenges. Complex setup or integration issues can arise, but modern systems like Fuji Gemco are designed to overcome these hurdles easily.
Here are five common challenges and solutions in PLC automation:
- Complex Programming: User-friendly software simplifies PLC coding.
- Integration Issues: Broad protocol support (e.g., Ethernet, Profibus) ensures compatibility.
- High Initial Costs: Long-term savings offset upfront investment.
- Maintenance Needs: Durable PLCs reduce upkeep, like Fuji Gemco’s systems.
- Skill Gaps: Training and intuitive interfaces empower operators.
These solutions make PLC automation accessible and practical.
Fuji Gemco: Your PLC Automation Partner
PLC automation is the key to modern industrial success, and Fuji Gemco leads the way with world-class solutions. Our PLC automation systems, featuring high-speed PLCs and NISDAS SCADA software, deliver precision, safety, and efficiency in steel, sugar, and power industries. Our systems empower your operations with a 6-nanosecond CPU, unlimited tags, and robust network support.
Ready to transform your plant? Visit Fuji Gemco’s website or contact us for a demo today.


